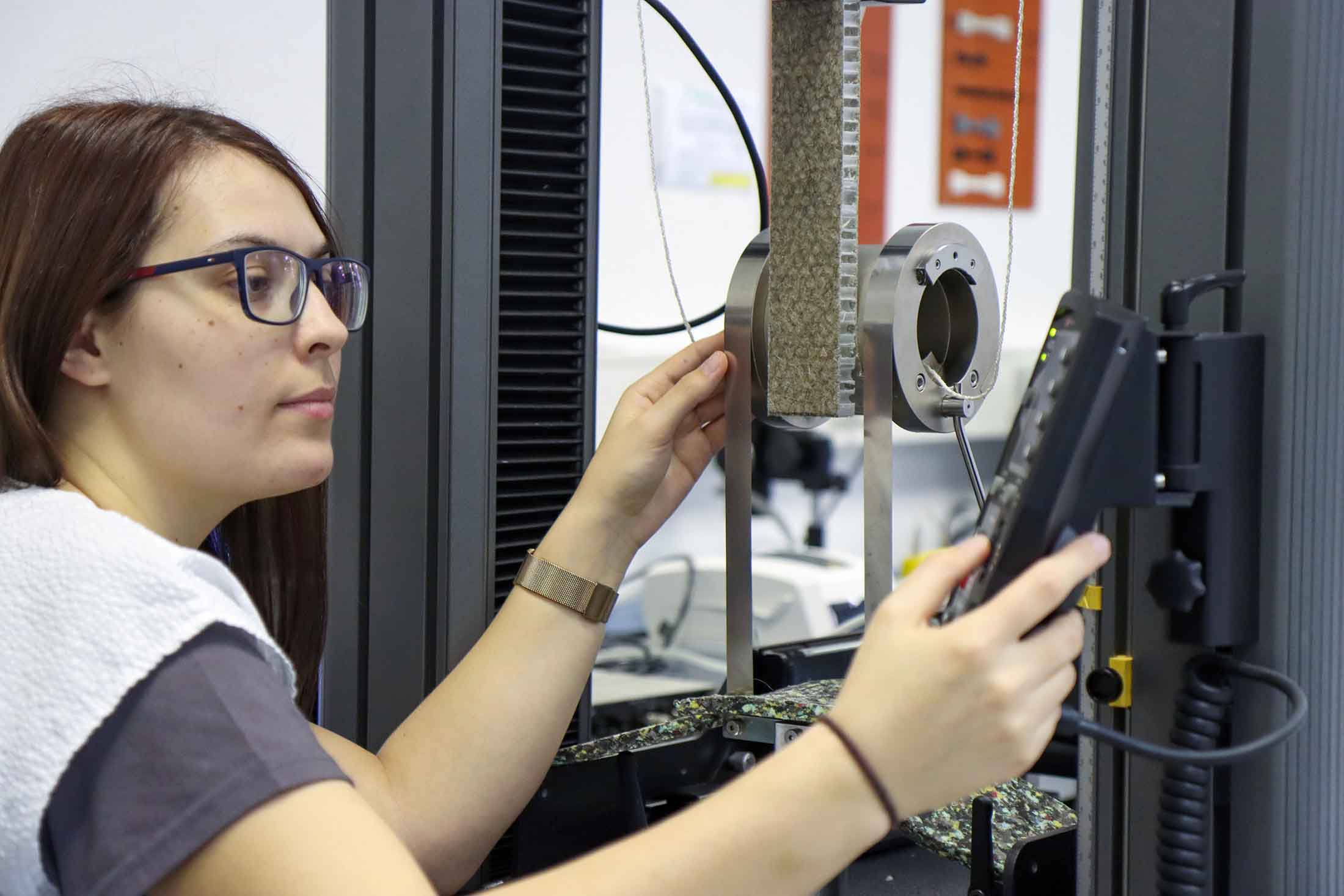

OMPG employee Jenny Bendwich uses the drum peeling test to check the strength of a sandwich structure with a honeycomb core. (Photo: OMPG / Steffen Beikirch)
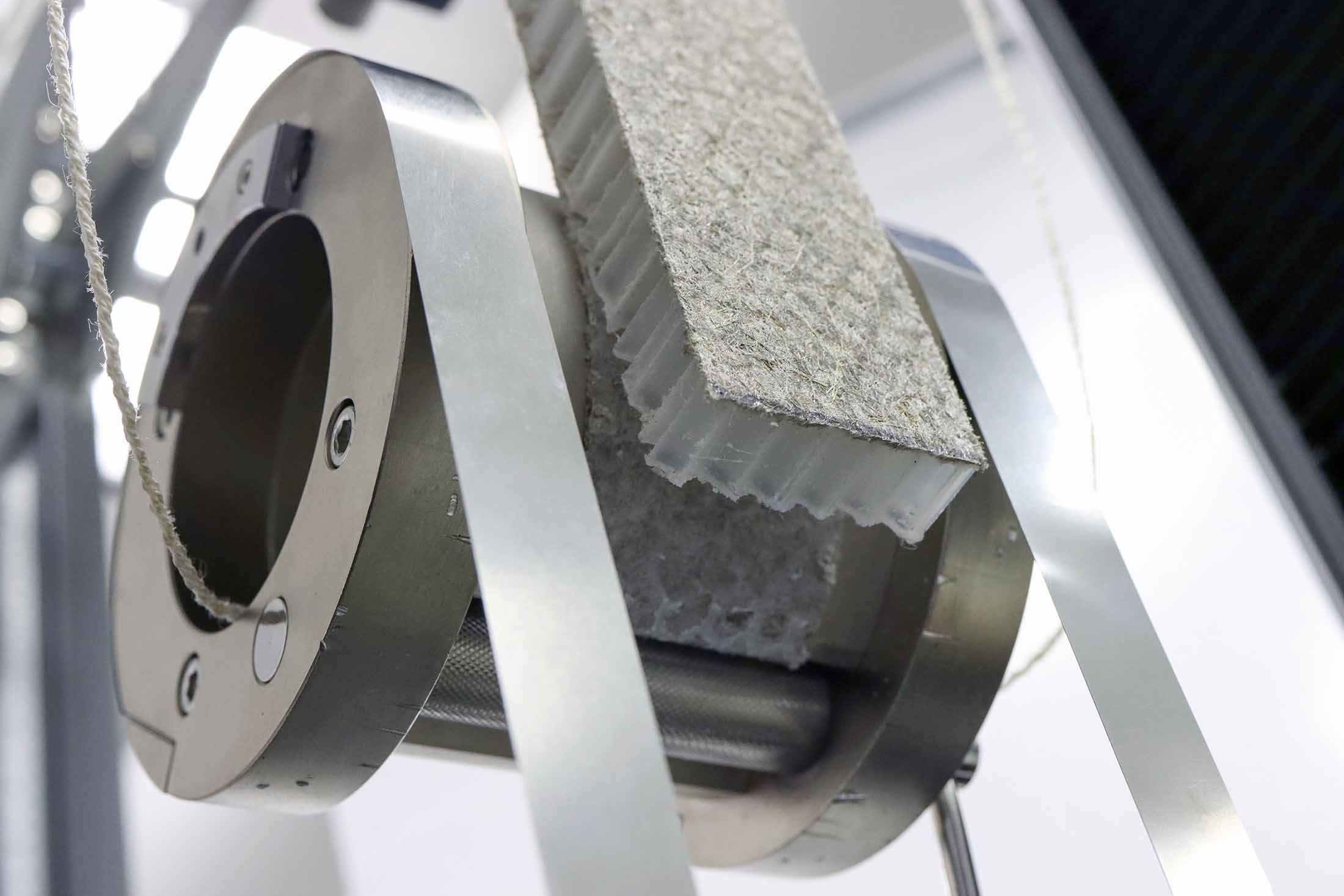

The combination of several different materials usually saves mass while still providing high rigidity and load-bearing capacity. The core of a sandwich material can consist of lightweight solid material, foam, or even honeycomb cores. It transfers any shear forces that occur and at the same time supports the cover layers. Sheet metal, wood, or fiber composites are often used for this purpose. This mix of materials opens up completely new possibilities for design and surface appearance. On the other hand, recycling is usually much more complex. And testing important material properties requires very specialized laboratory expertise.
What are typical sandwich tests?
Sandwich tests are special examinations that can be used to determine the mechanical properties and the bond between the individual layers of a sandwich material. The tests are important because they ensure that the sandwich components can withstand requirements such as bending, pressure, and tension, as well as various external conditions (heat, moisture, media influence). They help to identify weak points and guarantee safety in use. In short, sandwich tests are crucial for ensuring the quality and reliability of plastic and composite sandwich structures, especially in applications such as aerospace, automotive, construction, and mechanical engineering.
At OMPG, the following test methods are used for sandwich structures:
- Bending test
This test method is particularly relevant for components that are subject to bending stress. The aim is to determine the maximum bending stress that the material can withstand before it fails. The test can be performed as a 3- or 4-point test with spans of up to 1000 mm. - Drum peel test
In the drum peel test, peel forces are applied to the bonding layers of a sandwich. It provides information about the adhesive strength of the layers and helps to identify potential weak points. - Shear test
The shear test determines the shear strength of the core material in order to evaluate its load-bearing capacity under lateral stress. - Further tests
In addition, various core and cover layer materials can be characterized in the OMPG laboratories. The portfolio ranges from a wide variety of chemical analysis methods to fire tests, thermal tests, surface tests, and resistance to light, heat, and climate stress.
Would you like to learn more about our testing methods or receive individual advice?
Simply call us at +49 3672 379-341 or send an email to prueflabor@ompg.de.



![[Translate to English:] [Translate to English:]](/fileadmin/_processed_/b/b/csm_brandpruefungen-und-elektroanwendungen_7036bf8d6b.jpg)

![[Translate to English:] [Translate to English:]](/fileadmin/_processed_/8/a/csm_biologische-pruefungen_b330c70d45.jpg)


